
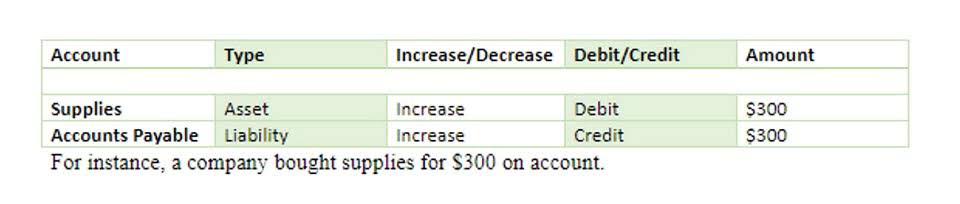
Ideally, this central repository will provide access to the document, amortization schedules, critical date alerts, journal entries, and footnote disclosures all at once. As companies adopt the new standards, they need to record all leases on the balance sheet, which, for public companies, has resulted in an average liability increase of 1,475%. This may require companies to monitor correspondence with lease counterparties, internal approvals of contract modifications and other means by which modifications can be affected.
- In the event of a lease modification, the lessor should determine whether such a modification should be accounted for as a separate lease.
- It’s important to know how to properly calculate the lease liability amortization schedule whether you plan to use Excel or lease accounting software.
- Initial direct costs are included in the net investment in the lease, with the exception of manufacturers or dealer lessors.
- This occurs when, for whatever reason, the lessee abruptly terminates the lease.
- In a sale-leaseback transaction, the lessee sells the asset to the buyer/lessor and enters into an agreement to lease the asset back from the buyer/lessor.
- Any difference between the net investment in the lease and the carrying value of the underlying asset is recognized as a gain or loss on the income statement.
Lease accounting under the old standards

Additional consideration should be given to the application of the 12-month rule. Where available, this rule can provide accelerated cost recovery and remove some of the uncertainty that often surrounds the treatment of these payments. The Handlery court did not, however, discuss a scenario where a lessor terminates a lease https://x.com/BooksTimeInc to sell the property. Like IFRS 16, GASB 87 also uses a single model approach, in which all leases are classified as finance leases.
Lease modifications – definition and accounting
It may be reasonable to use the general principle of “substance over form” and treat these as costs included in the general framework of lease termination payments. The court applied its lease termination analysis to the payments without regard to the contract language or the specific purpose for which the payments were designated. LE then remeasures the lease liability to reflect the revised lease payments of $30,000 annually for the remaining lease term of 7 years, using the revised incremental borrowing rate of 7%.

Reassessment of lease classification
- It is important to note this asset is classified as an intangible asset on the lessee’s books, rather than a fixed asset.
- This area of accounting has undergone many changes after recent pronouncements.
- Many companies are still using Excel for lease accounting instead of an accounting-focused software solution.
- The lease liability represents the lessee’s financial obligation over the lease term.
- Sales-type lease accounting occurs when the lease arrangement effectively transfers control of the underlying asset from the lessor to the lessee, which is considered akin to a sale.
Interest rate implicit in the lease is explained in the lessee accounting section. As noted below, initial direct costs are added to the initial net investment in the lease and the definition of implicit interest rate https://www.bookstime.com/articles/units-of-production-method takes this into account (IFRS 16.69). Unguaranteed residual value accruing to the lessor represents the sum that the lessor expects to recover from the value of the underlying asset at the lease’s conclusion.

The IRS could argue that the leases have an indefinite duration and the payment may not be amortized at all. Lessor accounting for lease modifications depends on the classification of the lease prior to the modification. For a modification that is not a separate lease, the lessee’s accounting depends on the nature of the modification. Finding a lease accounting solution that has custom reporting features is also important so you can create a report specifically for your organization’s needs.
In contrast to finance leases, manufacturer or dealer lessors do not recognise any selling profit upon entering an operating lease, as it is not considered equivalent to a sale (IFRS 16.86). In the event of a lease modification, the lessor should determine accounting for lease termination lessor whether such a modification should be accounted for as a separate lease. Criteria for such assessment are provided in paragraph IFRS 16.79 and are identical to those for lessees.